1. 加载过程 执行函数组件 Fiber 节点的 beginWork 工作,根据 tag 类型,进入 IndeterminateComponent 待定组件的逻辑处理【case IndeterminateComponent】:
每个函数组件的首次加载都是走的 IndeterminateComponent 分支逻辑,这是因为在创建函数组件 Fiber 的时候,react 没有更新它的 tag 值,所以它的首次 beginWork 工作就会进入 IndeterminateComponent 分支,在mountIndeterminateComponent 方法中才会更新它的 tag,使函数组件的Fiber在更新阶段执行 beginWork 时,能够进入正确的 FunctionComponent 分支。
1.1 mountIndeterminateComponent packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberBeginWork.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 function mountIndeterminateComponent ( _current, workInProgress, Component, renderLanes, const props = workInProgress.pendingProps; let value; let hasId; # 调用函数组件 value = renderWithHooks( null , workInProgress, Component, props, context, renderLanes, ); if ( !disableModulePatternComponents && typeof value === 'object' && value !== null && typeof value.render === 'function' && value.$$typeof === undefined ) { # 类组件的处理逻辑 【只是类组件现在已经不走这里了】 } else { # 函数组件处理 workInProgress.tag = FunctionComponent; # 创建子节点 reconcileChildren(null , workInProgress, value, renderLanes); return workInProgress.child; } }
首先取出当前函数组件FIber节点上的最新的props,方便函数组件加载的使用,然后调用renderWithHooks方法,这个方法会执行我们定义的函数组件,返回值就是函数中return的内容,也就是jsx内容【处理过后的react-element元素对象】。
1.1.1 renderWithHooks packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberHooks.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 export function renderWithHooks <Props , SecondArg >( current: Fiber | null, workInProgress: Fiber, Component: (p: Props, arg: SecondArg ) => any , props : Props , secondArg : SecondArg , nextRenderLanes : Lanes , ): any { renderLanes = nextRenderLanes; # 设置为当前渲染中的Fiber currentlyRenderingFiber = workInProgress; # 重置函数组件节点的数据 workInProgress.memoizedState = null ; workInProgress.updateQueue = null ; workInProgress.lanes = NoLanes; ReactCurrentDispatcher.current = current === null || current.memoizedState === null ? HooksDispatcherOnMount : HooksDispatcherOnUpdate; # 调用这个函数,即调用组件,循环生成Element对象, let children = Component(props, secondArg); renderLanes = NoLanes; currentlyRenderingFiber = (null : any); currentHook = null ; workInProgressHook = null ; didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdate = false ; # 返回函数组件的内容【reactElement对象】 return children; }
1.1.1.1 ReactCurrentDispatcher ReactCurrentDispatcher 对象是一个全局变量,它是在react源码中的react包定义的:
packages\react\src\ReactCurrentDispatcher.js
1 2 3 4 5 const ReactCurrentDispatcher = { current: (null : null | Dispatcher), }; export default ReactCurrentDispatcher;
然后将它包装在一个新的对象中:
packages\react\src\ReactSharedInternalsClient.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 const ReactSharedInternals = { ReactCurrentDispatcher, ReactCurrentCache, ReactCurrentBatchConfig, ReactCurrentOwner, }; export default ReactSharedInternals;
而shared包【通用工具包】会引入这个对象,然后暴露给全局:
packages\shared\ReactSharedInternals.js
1 2 3 import ReactSharedInternals from '../react/src/ReactSharedInternalsClient' export default ReactSharedInternals;
其他资源包就可以通过shared工具包来拿到这个对象,所以我们在函数组件加载时才能使用这个对象:
packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberHooks.js
1 2 3 import ReactSharedInternals from 'shared/ReactSharedInternals' ;const {ReactCurrentDispatcher, ReactCurrentBatchConfig} = ReactSharedInternals;
知道了 ReactCurrentDispatcher 对象的由来,我们才能更好地理解它的作用,因为函数组件的每个 hook 实际就是在调用这个对象中的同名方法,比如 useState:
packages\react\src\ReactHooks.js
1 2 3 4 export function useState (initialState ) const dispatcher = resolveDispatcher(); return dispatcher.useState(initialState); }
查看 resolveDispatcher:
1 2 3 4 5 function resolveDispatcher ( const dispatcher = ReactCurrentDispatcher.current; return dispatcher; }
其他的 hook 也是一样的原理。
1.1.1.2 函数组件调用 函数组件的加载核心就是执行一次函数的内容,理解起来也很简单。最后触发 return 关键字,这里的 jsx 内容会在 react 内部通过 jsxRuntime.jsx 方法进行处理,生成 react-element 对象,最后返回值就是创建的 react 元素对象。
最后返回生成的 react-element 对象,renderWithHooks 方法执行完成。
函数组件初始化执行完成后,就会更新函数组件Fiber节点的tag值为正确的类型FunctionComponent【后续逻辑函数组件节点便可以进入Function分支了】。
然后根据新建的value【react元素对象】创建子Fiber节点,最后返回子节点,函数组件的加载过程就基本完成了。
1.2 hooks的加载 根据上文得知,我们查看先前的 ReactCurrentDispatcher 对象
1 ReactCurrentDispatcher.current = HooksDispatcherOnMount
packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberHooks.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 const HooksDispatcherOnMount: Dispatcher = { readContext, useCallback: mountCallback, useContext: readContext, useEffect: mountEffect, useImperativeHandle: mountImperativeHandle, useLayoutEffect: mountLayoutEffect, useInsertionEffect: mountInsertionEffect, useMemo: mountMemo, useReducer: mountReducer, useRef: mountRef, useState: mountState, useDebugValue: mountDebugValue, useDeferredValue: mountDeferredValue, useTransition: mountTransition, useMutableSource: mountMutableSource, useSyncExternalStore: mountSyncExternalStore, useId: mountId, unstable_isNewReconciler: enableNewReconciler, };
例如我们在函数中依次使用useState、useEffect、useLayoutEffect,我们来看一下执行过程:
1.2.1 mountState packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberHooks.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 function mountState (initialState ) # hook加载工作 const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook(); if (typeof initialState === 'function' ) { initialState = initialState(); } hook.memoizedState = hook.baseState = initialState; const queue = { pending: null , lanes: NoLanes, dispatch: null , lastRenderedReducer: basicStateReducer, lastRenderedState: initialState, }; hook.queue = queue; const dispatch = queue.dispatch = dispatchSetState.bind(null , currentlyRenderingFiber, queue) # 返回值 return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch]; }
1.2.1.1 mountWorkInProgressHook 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 function mountWorkInProgressHook (Hook # hook对象 const hook: Hook = { memoizedState: null , baseState: null , baseQueue: null , queue: null , next: null , }; if (workInProgressHook === null ) { currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState = workInProgressHook = hook; } else { # 后面的hook对象添加到第一个hook的next属性上,形成一个单向链表 workInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next = hook; } return workInProgressHook; }
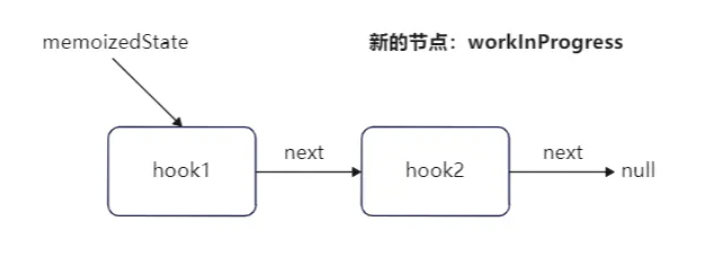
首先创建一个 hook 对象,workInProgressHook 默认为 null,它代表当前正在处理中的 hook 对象。
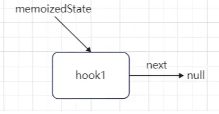
当前 useState 为函数组件中的第一个调用的 hook ,所以这时 workInProgressHook 肯定为 null:
将新建 hook 对象赋值给 workInProgressHook,表示为正在处理中的 hook 对象。
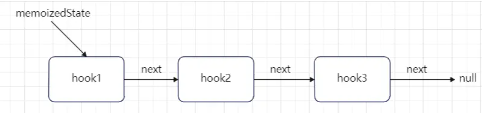
同时也将第一个 hook 对象赋值给当前函数组件 Fiber 节点的 memoizedState 属性。
此时函数组件 Fiber 节点的 memoizedState 属性指向为:
继续回到 mountState 方法中:
在 hook 新建完成之后,判断传入的参数 initialState 是否为函数,如果为函数则调用此函数,将结果赋值为新的 initialState。
然后设置 hook 对象的 memoizedState 和 baseState 属性为初始的数据 initialState。
接下来创建一个queue对象,这里要注意两个属性:
lastRenderedReducer:它是一个函数,作用是根据action和lastRenderedState计算最新的state。
1 2 3 4 5 function basicStateReducer (state, action ) return typeof action === 'function' ? action(state) : action; }
lastRenderedState:代表上一次渲染的state
然后更新 hook 对象的 queue 属性,同时设置 queue 对象的 dispatch 属性为一个修改函数 dispatchSetState
最后返回一个数组,这就是 useState hook 的返回值:一个初始state和一个修改函数。
1.2.2 mountEffect packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberHooks.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 function mountEffect ( create: ( ) => (( ) => void ) | void , deps : Array <mixed > | void | null , ): void { return mountEffectImpl( PassiveEffect | PassiveStaticEffect, # Passive标记对应的是useEffect HookPassive, create, deps, ); }
1.2.2.1 mountEffectImpl packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberHooks.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 function mountEffectImpl (fiberFlags, hookFlags, create, deps ): void # 创建的新的hook对象 const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook(); const nextDeps = deps === undefined ? null : deps; currentlyRenderingFiber.flags |= fiberFlags; hook.memoizedState = pushEffect( HookHasEffect | hookFlags, create, undefined , nextDeps, ); }
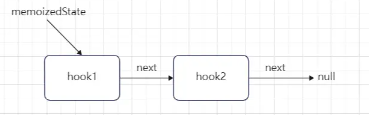
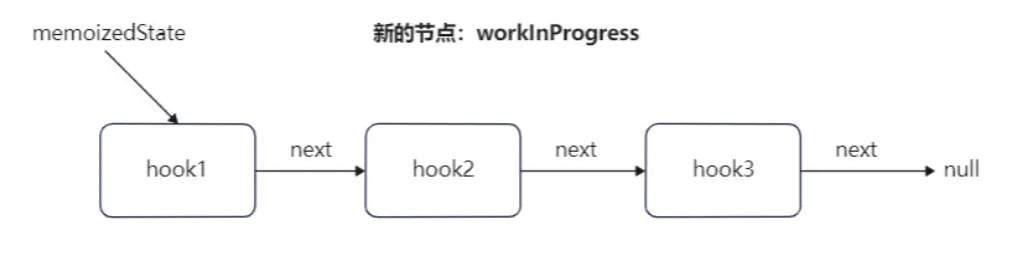
依然是先调用 mountWorkInProgressHook 创建一个 hook 对象,所以这里是先将第一个 hook 对象的 next 属性指向新建的 hook,然后再更新 workInProgressHook 的值为当前的 hook 对象。
此时函数组件Fiber节点的memoizedState属性指向为:
在 hook 创建完成之后,确定当前 hook 对象的 deps 依赖,因为我们传递的依赖为[],所以此时 deps 为一个空数组。然后更新当前 Fiber 节点的 flags 标记,最后设置 hook 对象的 memoizedState 属性内容,这里属性的结果为pushEffect 方法调用的返回值
1.2.2.2 pushEffect 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 function pushEffect (tag, create, destroy, deps ) # 创建副作用对象 const effect = { tag, create, destroy, deps, next: null , }; let componentUpdateQueue = currentlyRenderingFiber.updateQueue; if (componentUpdateQueue === null ) { componentUpdateQueue = createFunctionComponentUpdateQueue(); currentlyRenderingFiber.updateQueue = componentUpdateQueue; componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect = effect.next = effect; } else { const lastEffect = componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect; if (lastEffect === null ) { componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect = effect.next = effect; } else { const firstEffect = lastEffect.next; # 上一个effect的next属性指向新建的effect lastEffect.next = effect; # 新建的next属性指向第一个effect effect.next = firstEffect; componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect = effect; } } return effect; }
首先创建了一个effect对象,查看它的内容:
create 属性即为我们传入的回调函数。deps 属性是当前 useEffect hook的依赖。destory 属性为 undefined,它存储的是 useEffect hook返回的clean清理函数或者说销毁函数,但是它不是在这里赋值的,并且当前我们也没有返回这个函数。
然后取出当前函数组件 Fiber 节点的 updateQueue 属性内容赋值给变量 componentUpdateQueue。
然后判断 componentUpdateQueue 是否为 null:
为 null 时,然后调用 createFunctionComponentUpdateQueue 方法更新它的值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 function createFunctionComponentUpdateQueue (FunctionComponentUpdateQueue return { lastEffect: null , stores: null , }; }
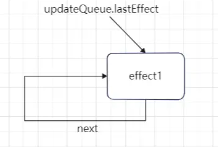
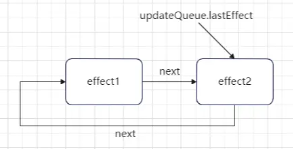
最后将当前创建的 effect 对象的 next 属性指向了自身,且同时更新 updateQueue.lastEffect 属性为当前 effect 对象,由此形成一个单向环状链表。
所以此时函数组件 Fiber 节点的 updateQueue 属性更新为:
pushEffect 方法最后,返回当前创建的 effect 对象。
再回到 mountEffectImpl 中:
1 hook.memoizedState = pushEffect()
所以 hook 对象的 memoizedState 属性值为一个 effect 对象。
从这里我们可以发现,虽然每个hook对象都是相同的属性,但是不同的 hook 类型它存储的内容却完全不同。
useState 创建的 hook 对象,它的 memoizedState 属性存储的为数据 state。useEffect 创建的 hook 对象,它的 memoizedState 属性存储的为一个 effect 对象。
1.2.3 mountLayoutEffect packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberHooks.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 function mountLayoutEffect ( create: ( ) => (( ) => void ) | void , deps : Array <mixed > | void | null , ): void { let fiberFlags: Flags = UpdateEffect; if (enableSuspenseLayoutEffectSemantics) { fiberFlags |= LayoutStaticEffect; } return mountEffectImpl(fiberFlags, HookLayout, create, deps); }
可以发现useEffect和useLayoutEffect共用了同一个加载方法 mountEffectImpl,所以它们会执行同样的逻辑处理。
hook 对象创建和处理,此时函数组件Fiber节点的memoizedState属性指向更新为:
effect 对象创建和处理,依然是 pushEffect 方法的调用:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 if (componentUpdateQueue === null ) { ... } else { # 第二次加载其他的effect时: const lastEffect = componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect; if (lastEffect === null ) { componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect = effect.next = effect; } else { const firstEffect = lastEffect.next; lastEffect.next = effect; effect.next = firstEffect; componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect = effect; } }
当前为第二个effect相关的 hook 处理,所以此时 Fiber.updateQueue【即componentUpdateQueue】是有值的,进入else分支处理。
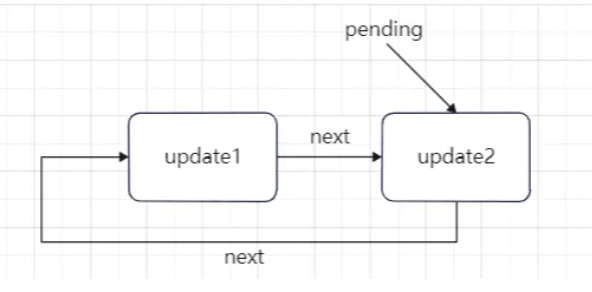
更新Fiber.updateQueue.lastEffect属性指向为当前新建的 effect2,将 effect2 的 next 属性指向为之前的 effect 对象。
此时函数组件 Fiber 节点的 updateQueue 属性指向更新为:
到此,函数组件加载阶段的 hooks 就处理完成。
1.3 commit阶段 前面全部的加载逻辑都是在 Fiber Reconciler 协调流程中执行的,即函数组件大部分的加载逻辑都是在 reconciler 协调流程中完成的【更新阶段同理】,还有剩下的一部分逻辑在 commit 阶段之中处理。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 function commitRootImpl ( scheduleCallback(NormalSchedulerPriority, () => { flushPassiveEffects(); }); commitBeforeMutationEffects() commitMutationEffects() commitLayoutEffects() }
commit 阶段的内容都是同步执行,在进入具体的执行之前,都会先调用 scheduleCallback 方法发起一个新的调度,即创建一个新的任务 task,最后会生成一个新的宏任务来异步处理副作用【即执行useEffect的回调钩子】。
上面是 useEffect 的回调处理,我们再查看 useLayoutEffect 的回调处理。
1.4 Layout阶段 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 function commitLayoutEffectOnFiber ( if ((finishedWork.flags & LayoutMask) !== NoFlags) { switch (finishedWork.tag) { case FunctionComponent: { commitHookEffectListMount(HookLayout | HookHasEffect, finishedWork); } } } }
1.4.1 commitHookEffectListMount packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberCommitWork.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 function commitHookEffectListMount (flags: HookFlags, finishedWork: Fiber ) # 当前函数组件的updateQueue属性,存储的是副作用链表 const updateQueue = finishedWork.updateQueue; const lastEffect = updateQueue !== null ? updateQueue.lastEffect : null ; if (lastEffect !== null ) { const firstEffect = lastEffect.next; let effect = firstEffect; do { if ((effect.tag & flags) === flags) { const create = effect.create; # 执行回调函数 effect.destroy = create(); } effect = effect.next; } while (effect !== firstEffect); } }
首先从当前函数组件 Fiber 节点取出它的 updateQueue 属性内容,在前面我们已经知道了 Fiber.updateQueue 存储的是副作用相关的链表,定义一个 lastEffect 变量存储 updateQueue.lastEffect 的内容,即最后一个 effect 对象。
判断 lastEffect 是否为 null ,如果 lastEffect 为 null,代表当前函数组件没有使用过 effect 相关的 hook。
当前肯定是有值的,继续向下执行。从 lastEffect.next 中取出第一个 effect 对象,开始按顺序循环处理副作用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 do { if ((effect.tag & flags) === flags) { const create = effect.create; effect.destroy = create(); } effect = effect.next; } while (effect !== firstEffect);
注意在执行之前有一个条件判断,只有存在 effect 相关的 flags 标记才会执行对应副作用回调。
而在之前 hook 加载是有进行设置的:
1 2 3 4 hook.memoizedState = pushEffect( HookHasEffect | hookFlags, )
在函数组件加载阶段时,每个 useEffect 和 useLayoutEffect 都有打上 HookHasEffect 的标记,表示在加载阶段都会默认执行一次。
需要注意的是:之前 commitHookEffectListMount 传入的是与 Layout 相关的 flags 标记。
1 commitHookEffectListMount(HookLayout | HookHasEffect, finishedWork);
所以这里只有 layout hook 的回调才能执行,第一个 effect 对象对应的是 useEffect,不满足判断条件
从当前 effect 对象的 next 属性取出下一个 effect 对象,开始第二次循环。
第二个 effect 对象对应的是 useLayoutEffect,满足判断条件,执行它的回调函数。
1 2 3 const create = effect.create;effect.destroy = create();
到此 hook 相关的回调处理完成,函数组件加载逻辑全部执行完成。
2. 更新过程 2.1 dispatchSetState 当操作更新触发 setState 时, 就是触发之前 useState 加载返回的 dispatch 方法:
1 2 3 const dispatch = queue.dispatch = dispatchSetState.bind(null , currentlyRenderingFiber, queue)# 返回值 return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];
packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberHooks.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 function dispatchSetState <S , A >( fiber: Fiber, queue: UpdateQueue<S, A>, action: A, // state 1 const lane = requestUpdateLane(fiber); const update: Update<S, A> = { lane, action, hasEagerState: false , eagerState: null , next: (null : any), }; if (isRenderPhaseUpdate(fiber)) { enqueueRenderPhaseUpdate(queue, update); } else { # 调度之前的一个优化策略校验: eagerState const alternate = fiber.alternate; if (fiber.lanes === NoLanes && (alternate === null || alternate.lanes === NoLanes)) { const lastRenderedReducer = queue.lastRenderedReducer; if (lastRenderedReducer !== null ) { let prevDispatcher; try { const currentState: S = (queue.lastRenderedState: any); const eagerState = lastRenderedReducer(currentState, action); update.hasEagerState = true ; update.eagerState = eagerState; if (is(eagerState, currentState)) { # 如果state没变,组件不做更新。此处和useReducer对比下,useReducer还是会让函数组件更新 enqueueConcurrentHookUpdateAndEagerlyBailout(fiber, queue, update); return ; } } catch (error) { } finally { } } } const root = enqueueConcurrentHookUpdate(fiber, queue, update, lane); if (root !== null ) { const eventTime = requestEventTime(); scheduleUpdateOnFiber(root, fiber, lane, eventTime); entangleTransitionUpdate(root, queue, lane); } } }
2.1.1 eagerState 首先看 dispatchSetState 方法的整个结构和类组件的更新方法 enqueueSetState 基本相同,还有 react 应用的初始加载 updateContainer,其实一个react应用的更新场景就只有这三种,而它们的更新逻辑就是以下几个步骤:
获取更新优先级 lane。
创建 update 更新对象 。
将 update 更新对象添加到目标Fiber对象的更新队列中。
开启一个新的调度更新任务。
它们的区别主要在于函数组件这里在调度之前有一个eagerState优化策略校验:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 const currentState: S = (queue.lastRenderedState: any);const eagerState = lastRenderedReducer(currentState, action);update.hasEagerState = true ; update.eagerState = eagerState; if (is(eagerState, currentState)) { enqueueConcurrentHookUpdateAndEagerlyBailout(fiber, queue, update); return ; }
这个优化策略的作用是:调用 queue.lastRenderedReducer 方法,通过原来的 state 和当前传入的 action 参数,快速的计算出本次最新的 state 【即eagerState】,通过比较新旧 state 来判断数据是否变化,如果没有变化则可以跳过后续的更新逻辑,即不会开启新的调度更新任务。当前我们的 state 是有变化的,所以不满足优化策略,将继续向下执行更新。
2.1.2 enqueueConcurrentHookUpdate 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 export function enqueueConcurrentHookUpdate <S , A >( fiber: Fiber, queue: HookQueue<S, A>, update: HookUpdate<S, A>, lane: Lane, FiberRoot | null const concurrentQueue: ConcurrentQueue = (queue: any); const concurrentUpdate: ConcurrentUpdate = (update: any); enqueueUpdate(fiber, concurrentQueue, concurrentUpdate, lane); return getRootForUpdatedFiber(fiber); }
回到 dispatchSetState 方法中,最后还是会调用 scheduleUpdateOnFiber 函数进入更新的调度程序。
2.1.3 flushSyncWorkOnAllRoots 1 2 3 4 function processRootScheduleInMicrotask ( flushSyncWorkOnAllRoots(); }
在 microtask 结束时,flush 任何 pending 的同步 work。这必须放在最后,因为它执行实际的可能会抛出异常的渲染工作。
直接快进到performSyncWorkOnRoot方法中:
1 2 3 4 export function performSyncWorkOnRoot (root: FiberRoot, lanes: Lanes ): null let exitStatus = renderRootSync(root, lanes); }
调用renderRootSync方法,开始FiberTree的创建过程。
在这之前,还有一个处理要注意:把 concurrentQueues 的内容添加到 fiber 的 queue 中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 function renderRootSync ( prepareFreshStack() } function prepareFreshStack ( finishQueueingConcurrentUpdates() }
2.1.4 updateFunctionComponent 下面进入 beginWork 工作的 FunctionComponent 处理分支,开始函数组件的更新:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 function updateFunctionComponent ( current, workInProgress, Component, nextProps: any, renderLanes, let nextChildren; # 调用函数组件 nextChildren = renderWithHooks( current, workInProgress, Component, nextProps, context, renderLanes, ); # 函数组件默认的bailout策略,满足条件比较苛刻 if (current !== null && !didReceiveUpdate) { bailoutHooks(current, workInProgress, renderLanes); return bailoutOnAlreadyFinishedWork(current, workInProgress, renderLanes); } reconcileChildren(current, workInProgress, nextChildren, renderLanes); return workInProgress.child; }
可以看见 updateFunctionComponent 方法主要有两个处理:
调用renderWithHooks【函数组件加载也是调用了这个方法】。
判断是否满足Bailout优化策略,满足则进入优化逻辑,跳过本组件的更新。不满足,则执行正常的组件更新逻辑。
2.1.5 renderWithHooks 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 export function renderWithHooks <Props , SecondArg >( current: Fiber | null, workInProgress: Fiber, Component: (p: Props, arg: SecondArg ) => any , props : Props , secondArg : SecondArg , nextRenderLanes : Lanes , ): any { renderLanes = nextRenderLanes; currentlyRenderingFiber = workInProgress; workInProgress.memoizedState = null ; workInProgress.updateQueue = null ; workInProgress.lanes = NoLanes; ReactCurrentDispatcher.current =current === null || current.memoizedState === null ? HooksDispatcherOnMount : HooksDispatcherOnUpdate; let children = Component(props, secondArg); renderLanes = NoLanes; currentlyRenderingFiber = (null : any); currentHook = null ; workInProgressHook = null ; didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdate = false ; # 返回函数组件的内容【reactElement对象】 return children; }
在更新阶段时:
1 ReactCurrentDispatcher.current = HooksDispatcherOnUpdate
renderWithHooks 方法的重点依然是组件的调用 Component(),这里的逻辑依然只是重新调用一遍我们定义的函数,最后返回最新的jsx内容【即reactElement对象】
2.1.6 hooks的更新 首先查看 useState 的更新:
1 2 3 const HooksDispatcherOnUpdate = { useState: updateState, }
1 2 3 function updateState (initialState: ) return updateReducer(basicStateReducer, initialState); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 function updateReducer (reducer, initialArg, init? ) const hook = updateWorkInProgressHook(); }
2.1.7 updateWorkInProgressHook 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 function updateWorkInProgressHook (Hook let nextCurrentHook: null | Hook; if (currentHook === null ) { const current = currentlyRenderingFiber.alternate; if (current !== null ) { nextCurrentHook = current.memoizedState; } else { nextCurrentHook = null ; } } else { nextCurrentHook = currentHook.next; } let nextWorkInProgressHook: null | Hook; if (workInProgressHook === null ) { nextWorkInProgressHook = currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState; } else { nextWorkInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next; } if (nextWorkInProgressHook !== null ) { workInProgressHook = nextWorkInProgressHook; nextWorkInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next; currentHook = nextCurrentHook; } else { if (nextCurrentHook === null ) { throw new Error ('Rendered more hooks than during the previous render.' ); } currentHook = nextCurrentHook; const newHook: Hook = { memoizedState: currentHook.memoizedState, baseState: currentHook.baseState, baseQueue: currentHook.baseQueue, queue: currentHook.queue, next: null , }; if (workInProgressHook === null ) { currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState = workInProgressHook = newHook; } else { workInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next = newHook; } } return workInProgressHook; }
就像函数组件的hook在加载时都会调用一个 mountWorkInProgressHook 方法,生成一个hook链表。
而函数组件的hook在更新时也会调用一个 updateWorkInProgressHook 方法,生成对应的hook链表。
所以 updateWorkInProgressHook 方法的作用是:确定当前函数 Fiber 节点的 memoizedState 属性内容,也就是生成它的 hook 链表。
它的做法就是从 current 节点上取出函数组件加载时生成的 hook 链表,按顺序取出原来的 hook 对象,根据原来的对象信息创建生成新的 newHook 对象,最后按顺序一个一个添加到新的 Fiber 节点的 memoizedState 属性上。
注意: 这里是一个重点,如果没有清空 next 属性,那更新当前函数组件 Fiber 节点的 memoizedState 属性,直接拿到第一个 hook 对象,就可以拿到整个 hook 链表,然后后续的 hook 更新就不需要再调用 updateWorkInProgressHook 方法了。
但是函数组件为啥不能如此处理呢?
因为react不能保证开发者是一定按照规范来使用的 hook ,如果开发者将 hook 置于条件语句中,在更新阶段出现了原来 hook 链表中不存在的 hook 对象,则在渲染时就会发生异常,所以react在函数组件更新时需要主动中断 hook 对象的next属性指向,按原来的链表顺序重新一个一个添加,如果出现了不匹配的 hook 对象,就会主动抛出异常,提示用户:
1 2 3 if (nextCurrentHook === null ) { throw new Error ('Rendered more hooks than during the previous render.' ); }
2.1.8 计算state 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 function updateReducer <S , I , A >( reducer: (S, A ) => S , initialArg : I , init ?: I => S , ): [S, Dispatch<A>] { const hook = updateWorkInProgressHook(); const queue = hook.queue; if (queue === null ) { throw new Error ( 'Should have a queue. This is likely a bug in React. Please file an issue.' , ); } queue.lastRenderedReducer = reducer; const current = currentHook; let baseQueue = current.baseQueue; const pendingQueue = queue.pending; if (pendingQueue !== null ) { if (baseQueue !== null ) { const baseFirst = baseQueue.next; const pendingFirst = pendingQueue.next; baseQueue.next = pendingFirst; pendingQueue.next = baseFirst; } current.baseQueue = baseQueue = pendingQueue; queue.pending = null ; } if (baseQueue !== null ) { const first = baseQueue.next; let newState = current.baseState; let newBaseState = null ; let newBaseQueueFirst = null ; let newBaseQueueLast = null ; let update = first; # 循环处理update更新对象 do { const updateLane = removeLanes(update.lane, OffscreenLane); const isHiddenUpdate = updateLane !== update.lane; const shouldSkipUpdate = isHiddenUpdate ? !isSubsetOfLanes(getWorkInProgressRootRenderLanes(), updateLane) : !isSubsetOfLanes(renderLanes, updateLane); if (shouldSkipUpdate) { const clone: Update<S, A> = { lane: updateLane, action: update.action, hasEagerState: update.hasEagerState, eagerState: update.eagerState, next: (null : any), }; if (newBaseQueueLast === null ) { newBaseQueueFirst = newBaseQueueLast = clone; newBaseState = newState; } else { newBaseQueueLast = newBaseQueueLast.next = clone; } currentlyRenderingFiber.lanes = mergeLanes( currentlyRenderingFiber.lanes, updateLane, ); markSkippedUpdateLanes(updateLane); } else { if (newBaseQueueLast !== null ) { const clone: Update<S, A> = { lane: NoLane, action: update.action, hasEagerState: update.hasEagerState, eagerState: update.eagerState, next: (null : any), }; newBaseQueueLast = newBaseQueueLast.next = clone; if (update.hasEagerState) { newState = ((update.eagerState: any): S); } else { const action = update.action; newState = reducer(newState, action); } } update = update.next; } while (update !== null && update !== first); if (newBaseQueueLast === null ) { newBaseState = newState; } else { newBaseQueueLast.next = (newBaseQueueFirst: any); } # 【重点】如果对某一个状态多次修改的最终结果是无变化,则会设置全局变量ReceivedUpdate为false,方便后续进入Bailout策略 if (!is(newState, hook.memoizedState)) { markWorkInProgressReceivedUpdate(); } hook.memoizedState = newState; hook.baseState = newBaseState; hook.baseQueue = newBaseQueueLast; queue.lastRenderedState = newState; } const dispatch: Dispatch<A> = (queue.dispatch: any); return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch]; }
在 updateWorkInProgressHook 方法调用完成之后,返回值就是 useState 对应的hook对象:
取出hook对象的queue队列,如果queue为null,则会抛出错误:
1 2 3 4 5 if (queue === null ) { throw new Error ( 'Should have a queue. This is likely a bug in React. Please file an issue.' , ); }
后面的逻辑看似比较多,但其实比较简单,而且和this.setState计算state的逻辑基本一致。
它的核心逻辑: 按顺序正向循环 update 更新队列,定义一个变量 newState 来存储最新的 state,然后根据原来 state 和 update 对象里面的信息计算最新的数据更新变量 newState,每循环一次就会从 update 对象的 next 属性取出下一个参与计算的 update,直接到所有的 update 处理完成。
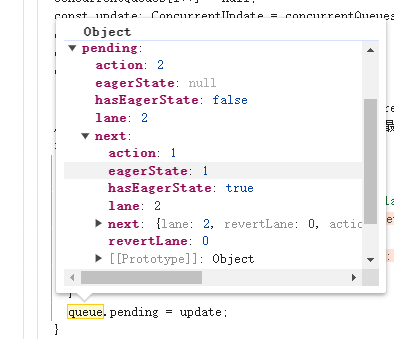
当前 pendingQueue 结构【单向环状链表】:
在类组件中,会根据pendingQueue的内容重构生成一个新的单向链表,不再是环状,有明确的结束。
和类组件不同的是,函数组件这里并没有额外处理pendingQueue,而是直接复制给baseQueue,从baseQueue.next取出第一个update对象【即first】开始计算state。
所以函数组件这里的do while循环多了一个结束的判断条件,就是不能等于first,不然就会陷入无限循环:
1 2 3 do { } while (update !== null && update !== first)
然后就是函数组件计算state的逻辑:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 if (update.hasEagerState) { newState = ((update.eagerState: any): S); } else { const action = update.action; newState = reducer(newState, action); }
如果eagerState存在,则直接使用eagerState的值为新的state。
如果不存在,则调用reducer【basicStateReducer】,根据最新的newState和当前update对象的action重新计算state。
循环结束,在更新state之前,还有一个校验需要注意:
1 2 3 4 # 【重点】如果对某一个状态多次修改的最终结果是无变化,则会设置全局变量ReceivedUpdate为false,方便后续进入Bailout策略 if (!is(newState, hook.memoizedState)) { markWorkInProgressReceivedUpdate(); }
在针对一个状态的批量处理之后,有一个状态变化的校验,针对的是函数组件内部的 Bailout 策略。
即如果对某一个状态多次修改的最终结果是无变化,则会设置全局变量 ReceivedUpdate 为 false,表示改组件没有更新的内容,这样就可以在 renderWithHooks 方法执行完成后,进入 Bailout 策略。
然后更新 hook 对象的 memoizedState 属性为最新的 newState:
1 2 hook.memoizedState = newState;
到此,useState hook 的更新程序执行完成,最后返回结果:
1 2 return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];
同时这里我们也可以明白:函数组件 useState hook 能够缓存变量结果的原因,因为它的 state 存储在 hook 对象的属性之中,并且这个属性可以在函数组件重新渲染过程中得到更新。
2.2 updateEffect 1 2 3 4 5 6 function updateEffect ( create: ( ) => (( ) => void ) | void , deps : Array <mixed > | void | null , ): void { return updateEffectImpl(PassiveEffect, HookPassive, create, deps); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 function updateEffectImpl (fiberFlags, hookFlags, create, deps ): void const hook = updateWorkInProgressHook(); const nextDeps = deps === undefined ? null : deps; let destroy = undefined ; if (currentHook !== null ) { const prevEffect = currentHook.memoizedState; destroy = prevEffect.destroy; if (nextDeps !== null ) { const prevDeps = prevEffect.deps; if (areHookInputsEqual(nextDeps, prevDeps)) { hook.memoizedState = pushEffect(hookFlags, create, destroy, nextDeps); return ; } } } currentlyRenderingFiber.flags |= fiberFlags; hook.memoizedState = pushEffect( HookHasEffect | hookFlags, create, destroy, nextDeps, ); }
首先依然是调用一个 updateWorkInProgressHook 方法,前面已经详细讲解了它的作用。所以这里调用此方法后,就会新建一个 newHook 对象,添加到第一个 hook 对象的 next 属性之上,形成一个链表,后续如果还有新的 newHook 对象则继续执行同样的逻辑。
此时函数 Fiber 节点的 memoizedState 属性内容为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 function areHookInputsEqual ( nextDeps: Array<mixed>, prevDeps: Array<mixed> | null, if (prevDeps === null ) { return false ; } for (let i = 0 ; i < prevDeps.length && i < nextDeps.length; i++) { if (is(nextDeps[i], prevDeps[i])) { continue ; } return false ; } return true ; }
当前我们依赖为一个空数组,所以满足第三种情况,直接返回 true。
到此,函数组件的第二个hook:useEffect更新完成。
2.3 updateLayoutEffect 1 2 3 4 5 6 function updateLayoutEffect ( create: ( ) => (( ) => void ) | void , deps : Array <mixed > | void | null , ): void { return updateEffectImpl(UpdateEffect, HookLayout, create, deps); }
可以发现 useEffect 和 useLayoutEffect 共用了同一个更新方法 updateEffectImpl,所以它们会执行同样的逻辑处理。
调用 updateWorkInProgressHook 方法:创建新 hook 对象,此时函数组件 Fiber 节点的 memoizedState 属性指向更新为:
判断 deps 依赖是否变化,如果变化则为对应的 effect 对象打上 HookHasEffect 的标记。
到此,函数组件更新阶段的 hooks 就处理完成。
2.4 总结 函数组件更新阶段主要有这两个重点逻辑:
根据 updateQueue 更新队列,循环计算 state,最后将最新的 state 数据存储到 Fiber.memoizedState 属性上并返回。
更新 Effect类 hook 时,判断依赖是否变化打上 HookHasEffect,最后会根据 effect.tag 值来决定本次更新是否执行回调。
useEffect 和 useLayoutEffect的区别:useLayoutEffect 是 useEffect 的一个变种,它们都是在 React 组件中处理副作用的方法。两者之间的主要区别在于它们的执行时机。
useEffect 的回调函数会在每次渲染结束后异步执行,这意味着它不会阻塞浏览器的渲染过程。换句话说,React 会在处理 useEffect 内部的状态更新之前,让浏览器先绘制屏幕。而 useLayoutEffect 的回调函数会在每次渲染结束后同步执行。这意味着它会阻塞浏览器的渲染过程,直到其执行完毕。因此,useLayoutEffect 可以在浏览器重新绘制屏幕之前触发。
需要注意的是,由于 useLayoutEffect 会阻塞浏览器的渲染过程,如果过度使用,可能会导致应用程序变慢,甚至引发性能问题。因此,在大多数情况下,应优先考虑使用 useEffect。只有在某些特定情况下,例如需要在 DOM 更新后立即进行某些操作,或者需要在用户看到渲染结果之前进行某些操作,才考虑使用 useLayoutEffect。