1 2 3 4 5 root.finishedWork = finishedWork; root.finishedLanes = lanes; finishConcurrentRender(root, exitStatus, finishedWork, lanes);
2. commit阶段 - finishConcurrentRender 2.1 finishConcurrentRender packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberWorkLoop.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 function finishConcurrentRender ( root: FiberRoot, exitStatus: RootExitStatus, finishedWork: Fiber, lanes: Lanes, commitRootWhenReady( root, finishedWork, workInProgressRootRecoverableErrors, workInProgressTransitions, workInProgressRootDidIncludeRecursiveRenderUpdate, lanes, workInProgressDeferredLane, ); }
2.2 commitRootWhenReady 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 function commitRootWhenReady ( root: FiberRoot, finishedWork: Fiber, recoverableErrors: Array<CapturedValue<mixed>> | null, transitions: Array<Transition> | null, didIncludeRenderPhaseUpdate: boolean, lanes: Lanes, spawnedLane: Lane, commitRoot( root, recoverableErrors, transitions, didIncludeRenderPhaseUpdate, spawnedLane, ); }
2.3 commitRoot 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 function commitRoot ( root: FiberRoot, recoverableErrors: null | Array<CapturedValue<mixed>>, transitions: Array<Transition> | null, didIncludeRenderPhaseUpdate: boolean, spawnedLane: Lane, const previousUpdateLanePriority = getCurrentUpdatePriority(); const prevTransition = ReactCurrentBatchConfig.transition; try { ReactCurrentBatchConfig.transition = null ; setCurrentUpdatePriority(DiscreteEventPriority); commitRootImpl( root, recoverableErrors, transitions, didIncludeRenderPhaseUpdate, previousUpdateLanePriority, spawnedLane, ); } finally { ReactCurrentBatchConfig.transition = prevTransition; setCurrentUpdatePriority(previousUpdateLanePriority); } return null ; }
2.4 commitRootImpl 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 function commitRootImpl ( root: FiberRoot, recoverableErrors: null | Array<CapturedValue<mixed>>, transitions: Array<Transition> | null, didIncludeRenderPhaseUpdate: boolean, renderPriorityLevel: EventPriority, spawnedLane: Lane, const finishedWork = root.finishedWork; const lanes = root.finishedLanes; if ( (finishedWork.subtreeFlags & PassiveMask) !== NoFlags || (finishedWork.flags & PassiveMask) !== NoFlags ) { if (!rootDoesHavePassiveEffects) { rootDoesHavePassiveEffects = true ; pendingPassiveEffectsRemainingLanes = remainingLanes; pendingPassiveTransitions = transitions; scheduleCallback(NormalSchedulerPriority, () => { flushPassiveEffects(); return null ; }); } } const subtreeHasEffects = (finishedWork.subtreeFlags & (BeforeMutationMask | MutationMask | LayoutMask | PassiveMask)) !== NoFlags; const rootHasEffect = (finishedWork.flags & (BeforeMutationMask | MutationMask | LayoutMask | PassiveMask)) !== NoFlags; if (subtreeHasEffects || rootHasEffect) { const prevTransition = ReactCurrentBatchConfig.transition; ReactCurrentBatchConfig.transition = null ; const previousPriority = getCurrentUpdatePriority(); setCurrentUpdatePriority(DiscreteEventPriority); const prevExecutionContext = executionContext; executionContext |= CommitContext; ReactCurrentOwner.current = null ; const shouldFireAfterActiveInstanceBlur = commitBeforeMutationEffects( root, finishedWork, ); commitMutationEffects(root, finishedWork, lanes); resetAfterCommit(root.containerInfo); root.current = finishedWork; commitLayoutEffects(finishedWork, root, lanes); } else { root.current = finishedWork; } return null ; }
2.4.1 异步执行 passive effects 执行 useEffect 的 effects
2.4.2 进入 commit 阶段 1 executionContext |= CommitContext
2.4.3 beforeMutation阶段 - commitBeforeMutationEffects 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 export function commitBeforeMutationEffects ( root: FiberRoot, firstChild: Fiber, boolean focusedInstanceHandle = prepareForCommit(root.containerInfo); nextEffect = firstChild; commitBeforeMutationEffects_begin(); const shouldFire = shouldFireAfterActiveInstanceBlur; shouldFireAfterActiveInstanceBlur = false ; focusedInstanceHandle = null ; return shouldFire; }
初始化 nextEffect 变量,这里的 firstChild 代表第一个处理的节点为 hostFiber。
然后调用 commitBeforeMutationEffects_begin,开始递归遍历 FiberTree,处理有副作用的 Fiber 节点。
2.4.3.1 commitBeforeMutationEffects_begin 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 function commitBeforeMutationEffects_begin ( while (nextEffect !== null ) { const fiber = nextEffect; const child = fiber.child; if ( (fiber.subtreeFlags & BeforeMutationMask) !== NoFlags && child !== null ) { child.return = fiber; nextEffect = child; } else { commitBeforeMutationEffects_complete(); } } }
2.4.3.2 commitBeforeMutationEffects_complete 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 function commitBeforeMutationEffects_complete ( while (nextEffect !== null ) { const fiber = nextEffect; setCurrentDebugFiberInDEV(fiber); try { commitBeforeMutationEffectsOnFiber(fiber); } catch (error) { captureCommitPhaseError(fiber, fiber.return, error); } resetCurrentDebugFiberInDEV(); const sibling = fiber.sibling; if (sibling !== null ) { sibling.return = fiber.return; nextEffect = sibling; return ; } nextEffect = fiber.return; } }
commitBeforeMutationEffects_complete方法也是一个while循环,对当前Fiber节点执行flags标记对应的操作,即执行commitBeforeMutationEffectsOnFiber方法。执行完成后,如果当前Fiber节点存在sibling兄弟节点,则将兄弟节点设置为最新的nextEffect,退出当前函数,开启兄弟节点的begin工作。如果不存在兄弟节点,则将当前Fiber节点的父级节点设置为最新的nextEffect,执行父级节点的commitBeforeMutationEffects_complete工作。
根据上面可以看出,BeforeMutation阶段逻辑和之前创建FiberTree的逻辑基本相同,都是深度优先遍历的顺序从HostFiber根节点开始【自上而下】遍历处理每一个满足条件的Fiber节点,执行flags对应的副作用操作,即相似的begin和complete工作逻辑。这里主要的执行内容在commitBeforeMutationEffectsOnFiber方法之中。
注意,其实commit阶段中三个子阶段的逻辑:基本都是以这种逻辑方式来处理相关的副作用内容。
2.4.3.3 commitBeforeMutationEffectsOnFiber 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 function commitBeforeMutationEffectsOnFiber (finishedWork: Fiber ) const current = finishedWork.alternate; const flags = finishedWork.flags; switch (finishedWork.tag) { case FunctionComponent: { if (enableUseEffectEventHook) { if ((flags & Update) !== NoFlags) { commitUseEffectEventMount(finishedWork); } } break ; } case ForwardRef: case SimpleMemoComponent: { break ; } case ClassComponent: { if ((flags & Snapshot) !== NoFlags) { if (current !== null ) { const prevProps = current.memoizedProps; const prevState = current.memoizedState; const instance = finishedWork.stateNode; const snapshot = instance.getSnapshotBeforeUpdate( finishedWork.elementType === finishedWork.type ? prevProps : resolveDefaultProps(finishedWork.type, prevProps), prevState, ); instance.__reactInternalSnapshotBeforeUpdate = snapshot; } } break ; } case HostRoot: { if ((flags & Snapshot) !== NoFlags) { if (supportsMutation) { const root = finishedWork.stateNode; clearContainer(root.containerInfo); } } break ; } case HostComponent: case HostHoistable: case HostSingleton: case HostText: case HostPortal: case IncompleteClassComponent: break ; default : { if ((flags & Snapshot) !== NoFlags) { throw new Error ( 'This unit of work tag should not have side-effects. This error is ' + 'likely caused by a bug in React. Please file an issue.' , ); } } } if ((flags & Snapshot) !== NoFlags) { resetCurrentDebugFiberInDEV(); } }
进入 commitBeforeMutationEffectsOnFiber 方法后,发现只有 Snapshot 标记的副作用才会执行。
hostFiber 节点的 Snapshot 副作用是在 completeWork 工作中被标记的。
2.4.3.4 BeforeMutation阶段总结 所以BeforeMutation阶段最终只会执行这两种副作用:
触发类组件的getSnapshotBeforeUpdate钩子。
处理HostRoot类型节点【HostFiber】,清空#root容器内容, 方便下面Mutation阶段的DOM挂载。
2.4.4 mutation 阶段 - commitMutationEffects 前面我们已经知道了 MutationMask 的定义:
1 MutationMask = Placement | Update | ChildDeletion | ContentReset | Ref | Hydrating | Visibility;
而 MutationMask 就是代表 Mutation 阶段所需要执行的哪些副作用类型,虽然可以看到 MutationMask 集成了很多的副作用标记,但是 Mutation 阶段的重点内容:还是针对 Fiber 节点上 DOM 内容的处理,然后将最终的 DOM 内容渲染到页面。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 export function commitMutationEffects ( root: FiberRoot, finishedWork: Fiber, committedLanes: Lanes, inProgressLanes = committedLanes; inProgressRoot = root; commitMutationEffectsOnFiber(finishedWork, root, committedLanes); inProgressLanes = null ; inProgressRoot = null ; }
2.4.4.1 commitMutationEffectsOnFiber 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 function commitMutationEffectsOnFiber ( finishedWork: Fiber, root: FiberRoot, lanes: Lanes, const current = finishedWork.alternate; const flags = finishedWork.flags; switch (finishedWork.tag) { case FunctionComponent: case ForwardRef: case MemoComponent: case SimpleMemoComponent: { recursivelyTraverseMutationEffects(root, finishedWork, lanes); commitReconciliationEffects(finishedWork); if (flags & Update) { try { commitHookEffectListUnmount( HookInsertion | HookHasEffect, finishedWork, finishedWork.return, ); commitHookEffectListMount( HookInsertion | HookHasEffect, finishedWork, ); } catch (error) { captureCommitPhaseError(finishedWork, finishedWork.return, error); } if ( enableProfilerTimer && enableProfilerCommitHooks && finishedWork.mode & ProfileMode ) { try { startLayoutEffectTimer(); commitHookEffectListUnmount( HookLayout | HookHasEffect, finishedWork, finishedWork.return, ); } catch (error) { captureCommitPhaseError(finishedWork, finishedWork.return, error); } recordLayoutEffectDuration(finishedWork); } else { try { commitHookEffectListUnmount( HookLayout | HookHasEffect, finishedWork, finishedWork.return, ); } catch (error) { captureCommitPhaseError(finishedWork, finishedWork.return, error); } } } return ; } case ClassComponent: { recursivelyTraverseMutationEffects(root, finishedWork, lanes); commitReconciliationEffects(finishedWork); if (flags & Ref) { if (current !== null ) { safelyDetachRef(current, current.return); } } return ; } case HostComponent: { recursivelyTraverseMutationEffects(root, finishedWork, lanes); commitReconciliationEffects(finishedWork); if (flags & Ref) { if (current !== null ) { safelyDetachRef(current, current.return); } } if (supportsMutation) { if (finishedWork.flags & ContentReset) { const instance: Instance = finishedWork.stateNode; try { resetTextContent(instance); } catch (error) { captureCommitPhaseError(finishedWork, finishedWork.return, error); } } if (flags & Update) { const instance: Instance = finishedWork.stateNode; if (instance != null ) { const newProps = finishedWork.memoizedProps; const oldProps = current !== null ? current.memoizedProps : newProps; const type = finishedWork.type; const updatePayload: null | UpdatePayload = (finishedWork.updateQueue: any); finishedWork.updateQueue = null ; if (updatePayload !== null ) { try { commitUpdate( instance, updatePayload, type, oldProps, newProps, finishedWork, ); } catch (error) { captureCommitPhaseError( finishedWork, finishedWork.return, error, ); } } } } } return ; } case HostText: { recursivelyTraverseMutationEffects(root, finishedWork, lanes); commitReconciliationEffects(finishedWork); if (flags & Update) { if (supportsMutation) { if (finishedWork.stateNode === null ) { throw new Error ( 'This should have a text node initialized. This error is likely ' + 'caused by a bug in React. Please file an issue.' , ); } const textInstance: TextInstance = finishedWork.stateNode; const newText: string = finishedWork.memoizedProps; const oldText: string = current !== null ? current.memoizedProps : newText; try { commitTextUpdate(textInstance, oldText, newText); } catch (error) { captureCommitPhaseError(finishedWork, finishedWork.return, error); } } } return ; } case HostRoot: { recursivelyTraverseMutationEffects(root, finishedWork, lanes); commitReconciliationEffects(finishedWork); if (flags & Update) { if (supportsMutation && supportsHydration) { if (current !== null ) { const prevRootState: RootState = current.memoizedState; if (prevRootState.isDehydrated) { try { commitHydratedContainer(root.containerInfo); } catch (error) { captureCommitPhaseError( finishedWork, finishedWork.return, error, ); } } } } if (supportsPersistence) { const containerInfo = root.containerInfo; const pendingChildren = root.pendingChildren; try { replaceContainerChildren(containerInfo, pendingChildren); } catch (error) { captureCommitPhaseError(finishedWork, finishedWork.return, error); } } } return ; } default : { recursivelyTraverseMutationEffects(root, finishedWork, lanes); commitReconciliationEffects(finishedWork); return ; } } }
commitMutationEffectsOnFiber 方法内容很多,但是它的核心逻辑依然是switch case结构:根据当前Fiber节点tag值,对不同组件类型进行不同的逻辑处理。
要处理的组件类型有很多,我们主要掌握几个常见的组件类型处理逻辑:
FunctionComponent:函数组件。
ClassComponent:类组件。
HostComponent:DOM节点。
HostText:文本节点。
HostRoot:HostFiber根节点。
从上面几个组件类型的处理逻辑来看,它们都是一套相同的处理逻辑:
1 2 3 4 5 recursivelyTraverseMutationEffects(root, finishedWork, lanes); commitReconciliationEffects(finishedWork);
2.4.4.2 Mutation阶段执行顺序 1 2 3 4 5 6 commitMutationEffectsOnFiber => commit() recursivelyTraverseMutationEffects 这个方法中使用了循环,并且调用了上面的方法=> for () commitReconciliationEffects(finishedWork); commitPlacement(finishedWork);
所以Mutation阶段的执行顺序就可以表示为:
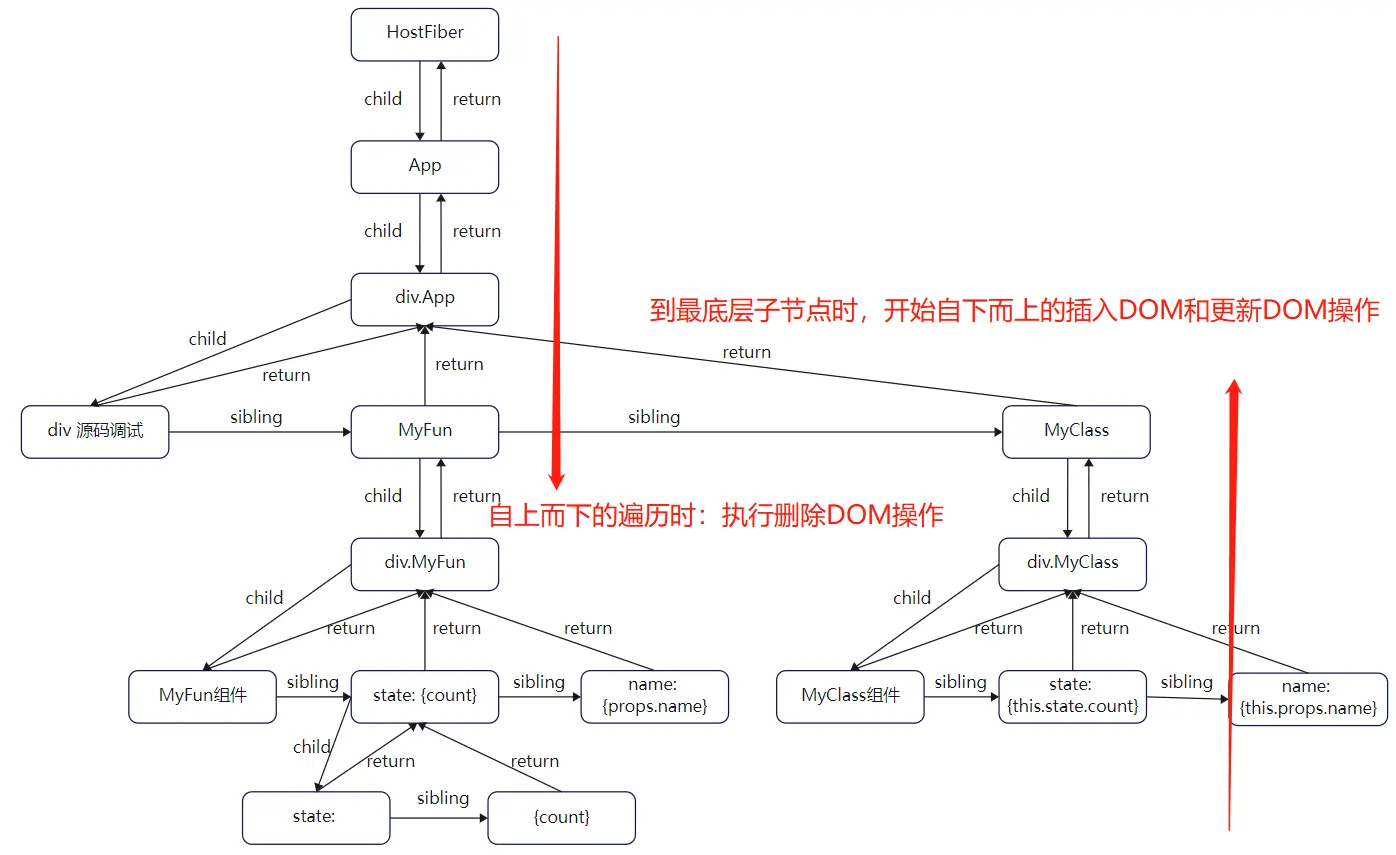
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Fiber顺序: HostFiber => commit for commit for commit for commit ... content content content
执行顺序为从上往下,通过这种递归遍历方式,可以发现HostFiber虽然是第一个进入commit逻辑的节点,但是它的content内容却是最后一个执行,也就是说在HostFiber的content内容处理完成之后,即代表完整的DOM树已经渲染到页面。实际上最后执行插入到页面的操作是在【fun App】组件节点上执行的,后续会有说明,这部分内容在第三章也有解释。
2.4.4.3 recursivelyTraverseMutationEffects 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 function recursivelyTraverseMutationEffects ( root: FiberRoot, // root parentFiber: Fiber, // HostFiber lanes: Lanes, # 删除标记,是否存在 const deletions = parentFiber.deletions; if (deletions !== null ) { for (let i = 0 ; i < deletions.length; i++) { const childToDelete = deletions[i]; try { commitDeletionEffects(root, parentFiber, childToDelete); } catch (error) { captureCommitPhaseError(childToDelete, parentFiber, error); } } } # 如果子节点树有副作用标记 if (parentFiber.subtreeFlags & MutationMask) { let child = parentFiber.child; while (child !== null ) { commitMutationEffectsOnFiber(child, root, lanes); child = child.sibling; } } }
根据上面的代码可以看出,recursivelyTraverseMutationEffects 方法主要就两个逻辑:
判断当前 Fiber 节点是否存在 deletions 删除标记,如果存在则循环 deletions,删除子节点对应DOM元素的内容。
遍历子树,递归调用 commitMutationEffectsOnFiber。
这里主要讲解第一点内容删除的逻辑,第二点遍历的内容就是前面 Mutation 阶段执行顺序的内容。commitDeletionEffects 方法,真实的删除逻辑比较复杂,删除一个DOM元素要考虑很多东西,这里我们不会展开 commitDeletionEffects 方法,但是还是要了解一下可能会造成的一些副作用影响:
执行子树所有组件的 unmount 卸载逻辑。
执行子树某些类组件的 componentWillUnmount 方法。
执行子树某些函数组件的 useEffect,useLayoutEffect等 hooks 的 destory 销毁方法。
执行子树所有 ref 属性的卸载操作。
这里将删除DOM的逻辑放在每个组件的第一个执行,也是非常必要的。因为Mutation阶段的核心就是DOM操作,如果对应的DOM都已经被删除了,那么也就没有必要再去执行剩下的修改更新了。
2.4.4.4 commitReconciliationEffects 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 function commitReconciliationEffects (finishedWork: Fiber ) const flags = finishedWork.flags; if (flags & Placement) { try { # 执行dom插入添加操作 commitPlacement(finishedWork); } catch (error) { captureCommitPhaseError(finishedWork, finishedWork.return, error); } finishedWork.flags &= ~Placement; } if (flags & Hydrating) { finishedWork.flags &= ~Hydrating; } }
commitReconciliationEffects 方法就是执行 DOM 的插入或者移动操作,判断当前 Fiber 节点是否存在 Placement 标记,存在就会执行 commitPlacement 方法,执行相关的 DOM 的操作。
2.4.4.5 commitPlacement 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 function commitPlacement (finishedWork: Fiber ): void if (!supportsMutation) { return ; } const parentFiber = getHostParentFiber(finishedWork); switch (parentFiber.tag) { # 普通DOM节点 case HostComponent: { const parent: Instance = parentFiber.stateNode; if (parentFiber.flags & ContentReset) { resetTextContent(parent); parentFiber.flags &= ~ContentReset; } const before = getHostSibling(finishedWork); insertOrAppendPlacementNode(finishedWork, before, parent); break ; } # 处理HostFiber节点的插入动作: case HostRoot: case HostPortal: { const parent: Container = parentFiber.stateNode.containerInfo; const before = getHostSibling(finishedWork); # 将离屏的DOM树插入到#div; 马上页面上显示出DOM内容 insertOrAppendPlacementNodeIntoContainer(finishedWork, before, parent); break ; } } }
能够执行 Placement 副作用的,只有两种组件节点 HostComponent 和 HostRoot。
对于 HostComponent 来说,就是常规的 DOM 插入和移动,即调用原生的 DOM 方法执行对应的逻辑:
1 2 3 parentNode.appendChild() parentNode.insertBefore()
mutation阶段总结 mutation 阶段的主要工作是:
对 DOM 内容的增删改操作,最后将构建完成的离屏 DOM 树渲染到页面。
针对函数组件触发 useInsertionEffect hook 的副作用以及 useLayoutEffect hook 的 destroy 方法。
针对类组件和普通 DOM 组件重置 ref 对象的内容。
2.4.5 layout 阶段 - commitLayoutEffects 前面我们已经知道了 LayoutMask 的定义:
1 LayoutMask = Update | Callback | Ref | Visibility;
而 LayoutMask 就是代表 Layout 阶段所需要执行的哪些副作用类型:
类组件的 componentDidMount/componentDidUpdate 生命周期钩子函数的执行。
类组件调用 this.setState 时传递的 callback 回调函数的会被保存到 Fiber 节点的 updateQueue 属性中在这里执行。
执行函数组件的 useLayoutEffect hook 回调。
可以说 Layout 阶段的主要内容:就是在DOM渲染完成后,执行函数组件和类组件定义的一些callback回调函数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 export function commitLayoutEffects ( finishedWork: Fiber, root: FiberRoot, committedLanes: Lanes, void inProgressLanes = committedLanes; inProgressRoot = root; nextEffect = finishedWork; # 又是begin 和complete工作逻辑 # 相当于递归循环触发每个组件的生命周期钩子函数 以及相关的 hooks 回调 commitLayoutEffects_begin(finishedWork, root, committedLanes); inProgressLanes = null ; inProgressRoot = null ; }
2.4.5.1 commitLayoutEffects_begin 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 function commitLayoutEffects_begin ( subtreeRoot: Fiber, root: FiberRoot, committedLanes: Lanes, const isModernRoot = (subtreeRoot.mode & ConcurrentMode) !== NoMode; while (nextEffect !== null ) { const fiber = nextEffect; const firstChild = fiber.child; # 说明子树存在副作用,需要更新nextEffect为子节点,进入下一级的循环 if ((fiber.subtreeFlags & LayoutMask) !== NoFlags && firstChild !== null ) { firstChild.return = fiber; nextEffect = firstChild; } else { # 说明副作用在自身节点了,进入complete阶段 commitLayoutMountEffects_complete(subtreeRoot, root, committedLanes); } } }
2.4.5.2 commitLayoutMountEffects_complete 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 function commitLayoutMountEffects_complete ( subtreeRoot: Fiber, root: FiberRoot, committedLanes: Lanes, while (nextEffect !== null ) { const fiber = nextEffect; if ((fiber.flags & LayoutMask) !== NoFlags) { const current = fiber.alternate; setCurrentDebugFiberInDEV(fiber); try { # 执行副作用 commitLayoutEffectOnFiber(root, current, fiber, committedLanes); } catch (error) { captureCommitPhaseError(fiber, fiber.return, error); } } # 当回到HostFiber时,代表循环完成,退出layout工作 if (fiber === subtreeRoot) { nextEffect = null ; return ; } # 存在兄弟节点,开始兄弟节点的工作 const sibling = fiber.sibling; if (sibling !== null ) { sibling.return = fiber.return; nextEffect = sibling; return ; } # 不存在兄弟节点,则返回父级节点 nextEffect = fiber.return; } }
2.4.5.3 commitLayoutEffectOnFiber 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 function commitLayoutEffectOnFiber ( finishedRoot: FiberRoot, current: Fiber | null, finishedWork: Fiber, committedLanes: Lanes, void if ((finishedWork.flags & LayoutMask) !== NoFlags) { # 根据组件类型:进行不同的处理 switch (finishedWork.tag) { # 1,函数组件的处理 case FunctionComponent: case ForwardRef: case SimpleMemoComponent: { if (!enableSuspenseLayoutEffectSemantics || !offscreenSubtreeWasHidden) { commitHookEffectListMount(HookLayout | HookHasEffect, finishedWork); } break ; } # 2,类组件的处理 case ClassComponent: { const instance = finishedWork.stateNode; if (finishedWork.flags & Update) { if (!offscreenSubtreeWasHidden) { if (current === null ) { # 触发componentDidMount 生命周期钩子函数【这类静态方法:是存储在instance对象原型上的】 instance.componentDidMount(); } else { const prevProps = finishedWork.elementType === finishedWork.type ? current.memoizedProps : resolveDefaultProps( finishedWork.type, current.memoizedProps); const prevState = current.memoizedState; # 触发componentDidUpdate 生命周期钩子函数 instance.componentDidUpdate( prevProps,prevState, instance.__reactInternalSnapshotBeforeUpdate, ); } } } # 取出当前组件节点的updateQueue更新对象 const updateQueue: UpdateQueue = finishedWork.updateQueue; if (updateQueue !== null ) { commitUpdateQueue(finishedWork, updateQueue, instance); } break ; } case HostRoot: { const updateQueue: UpdateQueue = finishedWork.updateQueue; if (updateQueue !== null ) { let instance = null ; if (finishedWork.child !== null ) { switch (finishedWork.child.tag) { case HostComponent: instance = getPublicInstance(finishedWork.child.stateNode); break ; case ClassComponent: instance = finishedWork.child.stateNode; break ; } } commitUpdateQueue(finishedWork, updateQueue, instance); } break ; } case HostComponent: { const instance: Instance = finishedWork.stateNode; if (current === null && finishedWork.flags & Update) { const type = finishedWork.type; const props = finishedWork.memoizedProps; # 针对一些特殊的DOM元素做加载处理:button,input等做自动聚焦,对Img图片做加载 commitMount(instance, type, props, finishedWork); } break ; } ... } } }
commitLayoutEffectOnFiber 方法依然是和前面两个阶段的逻辑一样,根据不同的组件节点进行不同的逻辑处理,这里我们还是理解几个重点组件类型即可。
layout阶段总结 在真实DOM加载完成后:
执行函数组件的useLayoutEffect hook的回调。
类组件执⾏ componentDidMount 或者 componentDidUpdate。。
由此可⻅,函数组件的 effects 和类组件中⽣命周期执⾏时机是不同的
FiberTree的切换 1 2 3 4 5 6 commitMutationEffects(root, finishedWork, lanes); # FiberTree的切换 root.current = finishedWork; commitLayoutEffects(finishedWork, root, lanes);
在 Mutation 阶段和 Layout 阶段之间还有一个重要处理没有说明,那就是 FiberTree 的切换。
通过前面我们已经知道,Mutation 阶段处理完成之后,页面就已经完成了真实的 DOM 渲染。所以此时finishedWork 就是最新的 FiberTree 以及存储着最新的 DOM 内容,在这里更新 current 的内容,主要有两个方面的作用:
保留最新的 Fiber 树结构,在下一次更新时就可以利用本次的 FiberTree 来做数据的复用以及差异对比。
对于类组件来说:当在 Layout 阶段执行 componentDidMount 或者 componentDidUpdate 生命周期钩子时就可以获取最新的 DOM 内容。
总结 到此为止,react18.2源码解析最重要的内容:即一个react应用的基本加载流程算是解析完成了,虽然其中一些逻辑描述可能不够准确,但整体来说还是比较符合。当然其中也有一些逻辑的细节并没有展开讲解,这是因为本身应用的加载流程就已经比较复杂了,如果在解析过程中每个逻辑都放在一起讲解,那文章的内容可能翻倍不止,阅读效果也会大打折扣。所以关于一些细节方面的逻辑处理会在新的章节里面展开讲解,比如类组件,函数组件的具体加载过程、hooks原理、合成事件等等。